|
2022년 12월 부로 Porometer사 장비 모델명이 아래와 같이 변경되었으니 참고 부탁드립니다.
변경 전 변경 후
POROLUX™ 50 POROLUX™ BP
POROLUX™ 100 POROLUX™ Cito L
POROLUX™ 200 POROLUX™ Cito M
POROLUX™ 500 POROLUX™ Cito
POROLUX™ 1000 POROLUX™ Revo
POROLIQ™ 1000 AQ POROLIQ™ AQ
POROLIQ™ 1000 ML POROLIQ™ ML

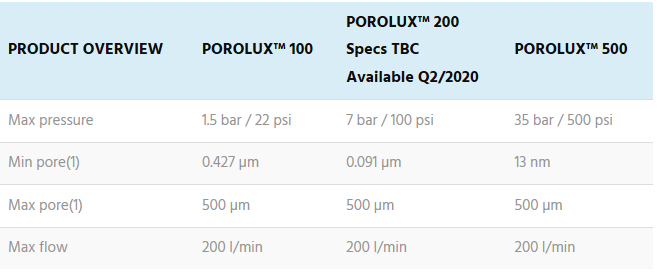
POROLUX™ 100
The POROLUX™ 100, 200 and 500 are gas liquid porometers based on the pressure scan method developed for the rapid measurement of through-pores in materials such as filters, nonwovens, textiles, paper, membranes, hollow fibres, etc.
PRESSURE AND FLOW RATES RANGE
The pressure scan-series contains instruments with pressure levels that go up to 1.5 bar (22 psi), such as the POROLUX™ 100, or go up to 35 bar (500 psi), such as the POROLUX™ 500. The maximum flow rate can be 200 l/min. For details please see the table of specifications for each model.
KEY FEATURES
•Gas-liquid displacement porometer based on the pressure scan method: the applied pressure and the resulting gas flow are measured continuously.
•Full flexibility with the highest accuracy in the full pressure range (up to 35 bar/ 500 psi).
•Very fast and reproducible measurements of first bubble point, maximum pore size, mean flow pore size, minimum pore size, pore size distribution and gas permeability.
•Ideal for quality control work.
PARAMETERS MEASURED
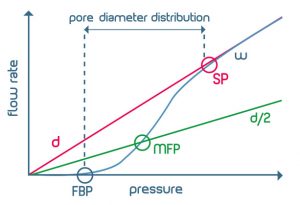
Measuring curves and resulting parameters in CFP
(w = wet curve, d = dry curve, d/2 = half-dry curve, FBP = largest pore, MFP = mean flow pore, SP = smallest pore)
In a typical CFP test a flow of pressurized gas is applied to the porous sample impregnated with the wetting liquid and the flow of gas through the sample, as the liquid is displaced out of the porous network, is measured. The “wet curve” represents the measured gas flow against the applied pressure.
Following the wet curve, the gas flow against the applied pressure on the dry sample (“dry curve”) is also measured. From data from the wet curve, the dry curve and the “half-dry curve” (dividing the flow values of the dry curve by 2) information about the porous network can be obtained.
•Bubble point
Maximum pore diameter
•Smallest pore size
Calculated at the pressure at which the dry curve meets the wet curve
•Mean flow pore diameter
Pore size at which 50 % of the total gas flow can be accounted (half the flow is through pores larger than this diameter)
•Gas permeability
In the same measurement it is possible to obtain the gas flow rate. If the material area and thickness are known, the gas permeability can also be accounted.
•Cumulative filter flow [SUM]
It shows which percentage of the flow (at the Y-axis) has passed through pores with a size larger than the value at the corresponding point at the X-axis. It is also known as filter efficiency.
•Differential filter flow [DIF]
It shows the percentage of flow (at the Y-axis), which has passed the pores with a corresponding size at the X-axis and the following size value at the same axis. According to ASTM this graph shows the so called “pore size frequency”.
•Pore size flow distribution [CDIF]
It shows the flow distribution normalized per unit of change in size (flow changes are divided by size changes). Sometimes it is also referred to as pore size distribution.
|










